The Fascinating World of Tourmaline: Nature’s Boron Recorder
The Fascinating World of Tourmaline: Nature’s Boron Recorder. In the enticing article, “The Fascinating World of Tourmaline: Nature’s Boron Recorder”, you’ll be immersed in the intriguing universe of gemology with a special emphasis on colored stones and pearls. At the heart of this exploration, we find the mineral tourmaline, a gemstone celebrated for its striking diversity and notable role as a revered collector’s item. With its unique chemical variations, a tourmaline can essentially echo extensive geological processes.
The sector zoning in a tourmaline crystal bears the detailed temperature history of its growth – effectively functioning as a geothermometer or geobarometer. As fascinating as that is, the masterpiece only gets better as it introduces boron as an integral part of tourmaline—making it a natural recorder of boron’s availability within the rock system. With photoluminescence spectroscopy having a crucial role separating natural from synthetic diamonds and discovering the heat-treated spinel, the article goes into how this technique can be applied to colored stones. Finally, the discerning reader is introduced to the Gemological Institute of America’s comprehensive educational offerings in gemology.
The Unique Nature of Tourmaline
Tourmaline as a significant gemstone
As an illustrious gemstone, tourmaline inspires fascination. Boasting a spectrum of vibrant colors, each jewel is an individual piece of art carefully crafted by Earth’s magnificent geological processes. Besides its visual enchantment, what sets tourmaline apart is its unique physical properties and complex general chemistry- making it an extraordinary subject in the field of gemology.
Collector’s item appeal of tourmaline
Deemed valuable not only for its use in adornments, the rich color palette and the distinct charm of tourmaline heighten its status as a sought-after collector’s item. Whether it is watermelon tourmaline’s bi-colored allure, Paraiba’s neon brilliance, or Dravite’s warm hues, tourmaline caters to every collector’s fantasy, uniting elements of rarity, aesthetics, and intrigue in one stunning piece.
Diverse chemical composition of tourmaline
The magic of tourmaline is wrapped within its diverse chemistry. At one look, you are looking at the crystallized memory of geological processes encoded in beautiful colors and patterns. These aren’t just gemstones, but mineralogical storytellers, each narrative as varied as the gemstone itself. From abundant silicon and aluminum to scarce lithium and rare-earth elements, the wide chemical range of tourmaline results in many gemological curiosities.
Sector Zoning in Tourmaline Crystals
Temperature history recording through sector zoning
Ever wondered how meteorological events get chronicled in natural history? Meet the sector zoning in tourmaline crystals, a geological marvel that records the complete temperature history of its growth. Acting as Earth’s thermometer and barometer, these chronicles encapsulate the entire trajectory of temperature fluctuations, providing invaluable insights into the past climatic patterns. Sotheby’s, Christie’s, and Phillips Showcase Rare Colored Diamonds in Recent Jewelry Auctions
Tourmaline as a geothermometer or geobarometer
Imagine a tiny crystal acting as a geothermometer or geobarometer. Tourmaline crystals do precisely that. Their careful study and observation help unravel the mysteries surrounding geological processes, including the fluctuations in Earth’s temperature and pressure system, making these gemstones instrumental in our quest to understand Earth’s history.
Insights into geological processes through tourmaline crystals
The interplay of the diverse elements within tourmaline crystals and their organized structural sectors provide scientists with precious insight into Earth’s geological past. It’s incredible how studying something as small as a tourmaline crystal can shed light on such humongous and complex processes. This continues to make tourmaline a gemological marvel, sparking interest and admiration among collectors and researchers alike.
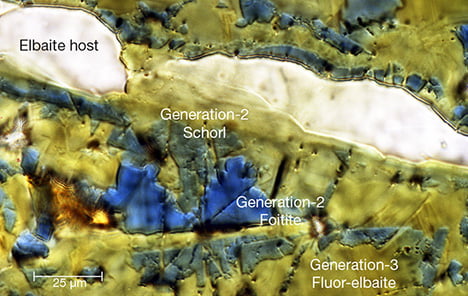
Boron and its Role in Tourmaline Formation
Tourmaline as nature’s boron recorder
Just as a phonograph records sound, tourmaline records boron, a chemical element that plays a pivotal role in its formation. Owing to boron’s fluid-mobile nature, its presence in tourmaline denotes the mobility and availability of boron in the rock environment, making tourmaline nature’s very own boron recorder.
Impact of fluid-mobile element boron on tourmaline formation
Boron doesn’t just dwell within a tourmaline crystal; it contributes substantially to its formation. The different amounts and availability of boron in the surrounding environment influence the gemstone’s composition and, consequently, its characteristics. This ability to reflect a fluid-mobile element like boron’s impact lends a whole new dimension to tourmaline’s allure in the gemological world. https://www.gia.edu/gia-bangkok
Reflection of boron availability in rock systems in tourmaline growth
To understand the availability of boron during a tourmaline’s growth phase, one needs to decipher the gemstone itself. A tourmaline’s boron content makes it an inherent indicator of boron availability in the geological formations, adding to its scientific significance and making its study all the more captivating for gemologists and geologists alike.
Tourmaline and Fluid Compositions Interplay
New growth of tourmaline through fluid compositions
The birth, life, and transformation of a tourmaline are intriguingly tied with the fluid compositions of its host rock environment. Various fluid compositions can instigate new growth phases within the tourmaline, each new phase representing a different chapter in the gemstone’s evolving life story.
Potential tourmaline dissolution and regrowth
Across periods of stability and turmoil, tourmaline showcases a divine dance of dissolution and regrowth. Essentially, tourmaline can cannibalize itself, dissolving under specific conditions, only to regrow when the environment becomes favorable. This cycle speaks a profound language of resilience and rebirth that is captivating to gemologists and collectors.
Possibility of another mineral’s replacement due to tourmaline-fluid interplay
The sophisticated dynamics between tourmaline and fluid compositions are so potent that they can lead to changes even beyond the tourmaline itself. The fine balance of these geological forces can even lead to tourmaline replacing another mineral wholly, testifying to the grandeur of Earth’s geological machinery at work.
The Mystery of Boehmite Needles in Corundum
Commonality of Boehmite needles in natural corundum
Corundum, the mining marvel behind gems like sapphire and ruby, also hosts its own mysteries. One such enigma is the commonality of the Boehmite needles in natural corundum. Preserve these needles in the form of inclusions and behold – the product is more compelling than ever.
Differentiation of natural and synthetic corundum through Boehmite needle study
The natural vs. synthetic debate cropped up time and again in gemology, and the Boehmite needles offer a valuable tool in this demise. The study of these needles in corundum has provided insights that help differentiate between natural and synthetic variations, bringing a great deal of clarity to the field and stirring interest among collectors and researchers.
Understanding Rose channels and their formation due to deformation twinning
Gemology is a generous host of mysteries, and the ones involving deformation twinning in natural corundum are among the most riveting. This twinning results in what are called Rose channels. The in-depth study of these channels, often misunderstood as Boehmite needle inclusions, has thrown light on many fascinating facets of gemology and mineralogy.
Photoluminescence Spectroscopy Applications
Importance of PL spectroscopy in separating natural and synthetic diamonds
Photoluminescence Spectroscopy, a vital tool in gemology, has revolutionized the way we discern between natural and synthetic diamonds. Employing properties of light, PL spectroscopy allows us to distinguish the subtle differences between the two, providing an accurate and non-destructive method of connoisseurship in gemology.
Use of PL spectroscopy in detecting treatments
Not just for detecting synthetic stones, PL spectroscopy is a potent tool for identifying treatments. The gem industry has seen instances of stones being altered or treated to enhance their appearance or value. Through PL spectroscopy, gemologists can detect such treatments, ensuring transparency and ethical practices within the gem trade.
Material identification and heat-treated spinel detection through PL spectroscopy
The prowess of PL spectroscopy extends to material identification and detection of heat-treated spinel. By analyzing the unique luminescence characteristics of gemstones, PL spectroscopy allows for the identification of gem species, and in the case of spinel, helps ascertain if it has been subjected to heat treatment.

Louminscent Centers of Rare Earth Elements
Role of REE in forming luminescent centers in Ca2+-bearing minerals
Under the gemological spotlight, the role of rare earth elements (REE) in forming luminescent centers in Ca2+-bearing minerals has emerged. These luminescent centers are essentially sites within a crystal structure where electron or hole traps create a unique glowing signature of the mineral – a characteristic that is making waves in gemological research.
Observations related to REE photoluminescence in cuprian liddicoatite tourmalines
In a fascinating development, REE photoluminescence has been observed in cuprian liddicoatite tourmalines from Mozambique. This discovery not only adds to the spectral allure of these tourmalines but brings a fresh perspective on the behavior of rare earth elements within gemstones.
Importance of studying REE in understanding mineral luminescence
Studying REE and their behavior in different mineralogical compositions is a valuable endeavor in unraveling the complexities of mineral luminescence. It helps in understanding how the Earth’s elemental resources contribute to the mystical glow displayed by various minerals, enhancing our understanding of gemstones beyond mere aesthetics.
Rare and Remarkable Tourmaline Discoveries
Exceptional tourmaline discoveries from around the world
From diverse landscapes across the globe, rare and remarkable tourmaline discoveries have been making headlines. Each discovery is proof of the untapped wonders that lie beneath, waiting to be unearthed, each tourmaline representing a unique chapter in the Earth’s geological narrative.
Scientific significance of unique tourmaline specimens
Beyond their beauty, these unique tourmaline specimens bear immense scientific significance. With a distinct chemical composition that offers a direct record of its geological lineage and climatic history, each one is like a time capsule providing a glimpse into Earth’s past, transforming our understanding of planetary evolution.
Impact of rare tourmaline forms on gemology
The discover of rare forms of tourmaline has exponentially expanded our knowledge of this gemstone and its potential in the field of study. Each discovery has refined our understanding of gem formation, cultivation, and enhancement, helping us appreciate these natural sculptures in new lights.

Tourmaline in the Gemological Education
Coverage of tourmaline in Gemological Institute of America (GIA) curriculum
In recognition of tourmaline’s scientific and aesthetic qualities, it holds a prominent place in the Gemological Institute of America’s (GIA) curriculum. Students of gemology study its formation, composition, enhancements, identification and more, equipping them with a comprehensive understanding of this multifaceted gemstone.
Graduate programs and online courses focusing on tourmaline
Several graduate programs and online courses focus on tourmaline, offering in-depth knowledge about this fascinating mineral. From digital lessons on its formation and identification techniques to field explorations, these programs cater to a variety of interests, aiding the growth of aspiring gemologists, seasoned scientists, or passionate collectors.
Importance of tourmaline knowledge in gemology careers
Gemology isn’t just about identifying and grading gemstones. It’s as much about interpreting their journey from the mantle to the jewelry box. This fact elevates the importance of understanding tourmaline in shaping a successful gemology career. A thorough knowledge of tourmaline serves as an asset to anyone planning to venture into this field, helping them understand and value the art of Earth’s everlasting creation.
Future of Tourmaline Research in Gemology
Potential areas for future research on tourmaline
Tourmaline’s complex formation and diverse compositions make it a promising subject for future research. Potential research areas might explore new sources of tourmalines, investigate their formations, delve into cause and effect of treatments, or undertake comparative studies of the different varieties.
The impact of new technologies on tourmaline study
The evolution of new technologies will revolutionize the study of tourmaline. Advanced tools can facilitate detailed analysis of composition, decipher subtle growth patterns, and ascertain geographical origin. This combination of traditional gemological knowledge and modern tools is set to propel tourmaline research to new heights.
Challenges and opportunities in tourmaline gemology
The path to deeper understanding of tourmaline presents both challenges and opportunities. The complexity of its formation and variations can be daunting. Simultaneously, this complexity fuels intrigue, fostering a wealth of opportunities for scientific investigation, education, and commercial entrepreneurship. As we brave this intricate dance of challenge and opportunity, our journey into the realms of tourmaline gemology promises to be nothing short of exceptional.

